
Chatbot vs Conversational AI: What’s the Key Differences?
- Riya Thambiraj
![Riya Thambiraj]()
- Artificial Intelligence
- Last updated on
AI is reshaping how businesses communicate with users. With conversational AI projected to surpass $61B in market value and chatbots expected to reach $46.6B by 2029, it’s becoming a core part of digital strategy for fast-growing teams.
As customer expectations rise, more companies are using automation to reduce support load, shorten response times, and create better user journeys across web, mobile, and voice. From guided product flows to voice-based support, the shift is already happening.
Who Is This Blog For?
This guide is for:
Founders validating automation ideas or building AI-driven UX
Product managers improving onboarding, feedback, or self-service support
CX teams and agencies aiming to scale without growing headcount
Teams in SaaS, e-commerce, healthcare, fintech, and more
Anyone exploring how to build bots or assistants that users actually engage with
What Does This Blog Covers?
We break down:
The key differences between traditional chatbots and modern AI assistants
Real-world examples across industries
Common use cases and when to combine both technologies
How to choose the right solution for your business
What we’ve learned building custom chat and voice solutions for startups and enterprises
This blog shares what works, what breaks, and how to make smarter decisions as you design your next support or engagement layer.
Let’s start with the basics. First, we’ll break down what a chatbot really is, and how it differs from conversational AI in both function and value.
What is a Chatbot?
A chatbot is a software application that simulates human conversation through text or voice. It helps users perform simple tasks, get quick answers, or navigate services without human intervention.
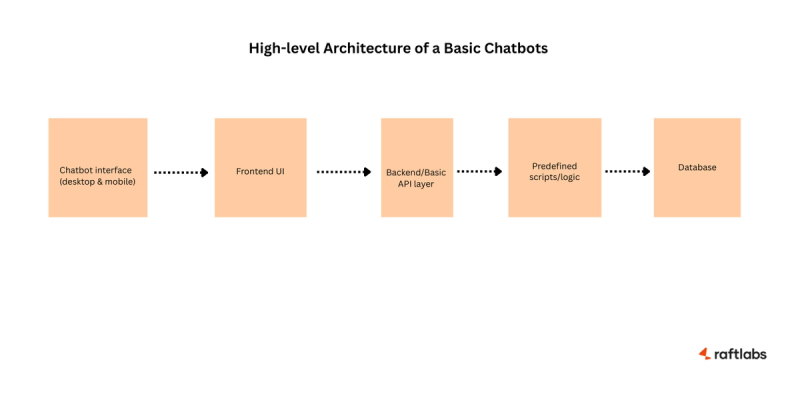
Chatbot Real-World Examples
1. Tidio (E-commerce and omnichannel support)
Online stores use Tidio bots to answer FAQs, greet new visitors, and recommend products in real time.
The chatbot works across channels like websites, Messenger, and Instagram, helping brands automate support and scale without hiring extra agents.
2. Drift (B2B lead capture and sales enablement)
Drift focuses on qualifying leads, booking demos, and personalizing conversations for B2B websites.
It’s a blend of chatbot and live chat, often used to shorten sales cycles and improve handoffs between marketing and sales teams.
3. Insomnobot-3000 (Healthcare-inspired engagement)
A simple, scripted chatbot designed to engage people during late-night hours. It doesn’t solve real problems but keeps users engaged with light conversation. A good example of using automation for emotional touchpoints.
4. Nightbot (Community moderation for streamers)
Popular with Twitch and YouTube creators, Nightbot helps automate live chat interactions.
It handles repetitive tasks like filtering spam, sharing preset links, or triggering FAQs, keeping streamers focused on their content.
Where are Chatbots Used Today?
E-commerce: Automating order tracking, product recommendations, and handling refund queries.
Healthcare: Scheduling appointments, sending medication reminders, and answering basic health questions.
Banking: Checking account balances, resetting passwords, and guiding users through simple transactions.
Tools like Insomnobot-3000 and Nightbot show how chatbots can handle niche use cases, but they often fall short when conversations require deep context or personalization.
Understanding these limitations is crucial as you explore the chatbot vs conversational AI differences for your business.
What is Conversational AI?
Conversational AI goes beyond the capabilities of traditional chatbots. It uses natural language processing (NLP), machine learning, and advanced algorithms to understand user intent, maintain context, and deliver more human-like conversations across web, mobile, and voice platforms.
Unlike basic chatbots, conversational AI can handle multi-turn dialogues and process ambiguous queries. It learns from vast datasets, which allows it to improve responses over time and personalize interactions based on user behavior.
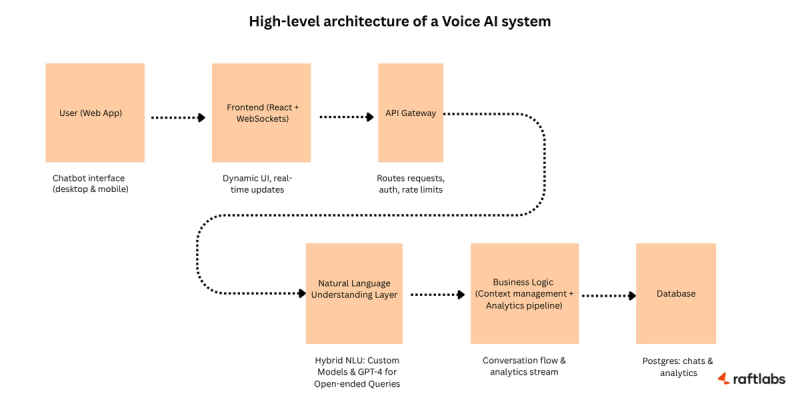
Read World Conversational AI Examples
There are hundreds of conversational AI platforms out there in the market that you can use in your business. But few of them are listed below
1. Lyro (Sales assistance in e-commerce)
Lyro sits on e-commerce sites, acting as a smart sales rep. It helps users find products, answers deeper support questions, and upsells based on behavior.
It keeps learning from interactions, so it improves performance over time without constant updates.
2. GPT-4 Turbo for knowledge-heavy support
Deployed by enterprise platforms to handle multi-turn support conversations, interpret vague questions, and surface context-aware responses from internal knowledge bases.
These assistants integrate with CRMs or databases to personalize every interaction.
3. D-ID AI agents in user-facing workflows
Used by e-learning and fintech platforms, these humanlike video agents offer walkthroughs, answer questions, and handle FAQs in a more visual, face-to-face format—helpful for improving trust and retention.
4. Siri (Multifunctional voice assistant)
Siri is built into Apple devices and handles voice commands like setting reminders, playing music, or calling contacts.
It shows how conversational AI works beyond chat—through voice, across apps, and with real-time task execution.
Where is Conversational AI making an Impact?
E-commerce: Guiding customers through complex buying journeys, upselling based on preferences, and resolving issues without agent handoff.
Healthcare: Offering symptom triage, mental health support, and integrating with EHR systems for appointment scheduling and patient updates.
Banking: Managing fraud detection conversations, offering investment advice, and supporting multilingual users across regions.
Examples like OpenAI’s GPT-4 Turbo and D-ID’s lifelike video agents show how these systems can power advanced virtual assistants that work seamlessly across channels and automate even high-value workflows.
As you explore chatbot vs conversational AI differences, understanding these capabilities will help you decide which technology aligns with your customer experience and operational goals.
Chatbot vs Conversational AI: Key Differences
Understanding the differences between chatbots and conversational AI can help you decide which solution aligns better with your customer experience and operational needs.
Here’s how they compare across key areas:
| Criteria | Chatbots | Conversational AI |
|---|---|---|
| Business Needs | Basic customer support, lead capture, FAQs | Personalized support, process automation, complex workflows |
| User Interactions | Simple, single-turn conversations | Multi-turn, context-aware dialogues |
| Integration Level | Minimal or no backend integration | Deep integration with CRMs and business systems |
| Channels | Single channel (web chat or app) | Omnichannel (web, mobile, voice, social platforms) |
| Scalability | Suitable for limited, predictable use cases | Designed for high-volume, dynamic interactions |
| Learning Ability | Static responses unless manually updated | Self-learning and adaptive with each interaction |
| Budget and Timeline | Lower cost and faster to deploy | Higher investment with long-term ROI |
1. Business Needs
Chatbots are a practical choice when the business problem is straightforward. If most user queries follow a clear pattern like checking delivery status, understanding pricing, or confirming office hours, rule-based chatbots can take over these tasks without needing a large investment.
They help deflect repetitive work and reduce the number of support tickets.
Conversational AI becomes necessary when user interactions go beyond one-step answers.
If your product or service involves guiding users through choices, qualifying them for offers, or helping them complete tasks across different systems, a simple chatbot will not hold up.
Conversational AI can maintain flow, adjust based on user input, and support multiple business goals within the same session. It shifts the role of automation from a support tool to a value driver.
2. User Interactions
Most chatbots work on a one-to-one exchange logic. A user types a query, and the system replies from a preset script.
If the user changes topic or provides incomplete input, the bot usually fails to respond properly or falls back to a generic message.
This is fine when users know exactly what to ask and when the bot’s scope is narrow.
Conversational AI allows for back-and-forth communication. It understands user context across multiple inputs, keeps memory of the conversation, and supports open-ended queries.
Users can refine or redirect the conversation midway. This reduces friction in use cases like application tracking, product comparison, or support troubleshooting, where users do not follow a perfect script.
4. Integration Level
Chatbots usually function in isolation. Most setups involve static content and workflows that do not pull live data or perform backend actions.
Connecting them to your database or CRM often requires significant customization, and even then, the logic remains rigid.
Conversational AI systems are designed to work as part of a broader digital infrastructure. They connect with your internal systems like order management tools, support ticket platforms, or sales CRMs.
This enables actions like checking real-time availability, updating a user record, or scheduling appointments based on current business logic.
These integrations turn conversations into actual transactions or updates inside your workflows.
5. Channels
Basic chatbots often exist on a single platform. They are built for the web widget, a WhatsApp line, or an in-app chat.
Each channel runs independently, and the system does not remember what the user said elsewhere. This is acceptable when support is needed only in one touchpoint.
Conversational AI works across platforms and keeps the thread going. A user can start chatting on the website, continue on a mobile app, and follow up via voice with the system remembering all past interactions.
This helps create a unified experience, especially in businesses where users interact across multiple devices or teams.
6. Scalability
Chatbots need manual work to scale. Every new feature, question, or exception must be accounted for with a rule, a reply, and a test.
As the use case complexity grows, so does the maintenance burden. This slows down iteration and limits the scope of automation.
Conversational AI scales through learning. As users ask new questions, the system adapts by recognizing patterns and improving its understanding.
This reduces the need to constantly update flows. It also enables teams to handle more queries without increasing headcount or development cycles. This makes the system more efficient as volume increases.
7. Learning Ability
A chatbot cannot improve by itself. It will keep replying based on the rules you gave it, even if those replies start feeling outdated or incorrect.
To improve performance, someone has to analyze interactions, find gaps, and manually update the flows. Over time, this becomes difficult to maintain at scale.
Conversational AI systems use data from each interaction to learn. If users ask questions that it cannot answer well, the model starts to recognize those gaps.
With regular training or fine-tuning, the system improves accuracy and relevance. It starts to anticipate follow-ups and tune its language to fit your brand tone or customer preferences. This makes long-term performance more reliable.
8. Budget and Timeline
Launching a chatbot is faster and more cost-effective. Most platforms offer templates or pre-built flows that work for common use cases.
If you are testing the idea of automated support or trying to offload first-level queries, this is the quickest way to validate impact.
Conversational AI requires more planning and investment. You need to map out real user journeys, set up integrations, and invest in training data or model configuration.
But once deployed, it requires less manual updating and offers more long-term value. It reduces load on support teams, improves resolution rates, and enhances user experience at a deeper level.
As you evaluate chatbot vs conversational AI differences, consider how much flexibility, scalability, and intelligence your customer interactions demand.
Check out: Our conversational AI development services to build chatbots and virtual assistants
Chatbot and Conversational AI: Types & Functionality
Both chatbots and conversational AI come in different forms, depending on how much flexibility, intelligence, and backend integration your workflows demand.
Here's a practical breakdown of the types and what they can do.
Types of Chatbots
Not all chatbots work the same way. Depending on how they’re built, each type has its strengths and limits.
Before deciding what to build, it’s helpful to understand the three common chatbot models used across industries today.
1. Rule-based chatbots
These bots operate on fixed scripts. Every question and every answer are mapped out in advance. The user clicks buttons or follows menu options to get to the response. There’s no guessing involved, and no flexibility either.
Rule-based bots are useful when your goal is to guide users through very predictable tasks, like filling out a form, checking business hours, or getting a refund policy.
They work well in situations where user behavior does not change much. But if the user goes off-script or types something unexpected, these bots cannot keep up.
2. AI-powered chatbots
This type uses basic natural language processing to understand user intent. Instead of clicking buttons, the user types freely, and the bot tries to figure out what they mean.
These AI powered chatbots are more flexible than rule-based ones. They can answer a wider range of queries and are better at handling small variations in phrasing.
However, they still operate within set boundaries. They are not great at remembering earlier parts of the conversation or adjusting the flow based on user history.
This makes them suitable for dynamic FAQs, form-filling with light personalization, or simple triage conversations that branch based on what the user says.
3. Hybrid chatbot models
A hybrid bot blends both approaches. It uses rules where control is important and brings in light AI to handle open input. This setup is often used in industries where consistency matters, like banking or insurance.
For example, the onboarding process might follow a strict script, but general support questions can be handled more flexibly.
Hybrid bots let companies explore conversational AI without giving up control over key flows. This model helps teams experiment safely, learn from real conversations, and decide where AI makes sense before scaling it further.
Check out: Our AI chatbot development services to build your AI powered chatbots.
Types of Conversational AI
Not all conversational AI systems work the same way. Depending on your user needs, platform strategy, and workflow complexity, you can choose from different types of assistants.
Here's a breakdown of the most common ones in real-world use.
1.Virtual assistants
These are intelligent, voice-first systems built to handle a wide range of tasks using natural conversation. Siri and Alexa are the most well-known examples. They work across devices and respond to spoken commands.
These assistants are useful for users who want quick answers or actions without touching a screen.
They can set reminders, answer questions, or control smart devices. Behind the scenes, they tap into multiple data sources and APIs to get things done.
Businesses can build similar systems for tasks like voice-based appointment booking or order tracking, especially in environments where hands-free interaction is valuable.
2. Multimodal bots
These bots can handle both text and voice within the same conversation. A user might speak a command, switch to typing, and then hear a response without breaking the flow.
This makes them ideal for use cases where users need flexibility. In healthcare, for example, a patient might talk to the bot during a check-in and then get follow-up instructions via text.
In retail, the user might search for a product by voice but finalize the order using buttons or text input. Multimodal bots make the experience seamless across interaction styles, which boosts usability in complex or high-stakes workflows.
3. Omnichannel AI agents
These systems run across multiple platforms (like websites, mobile apps, WhatsApp, SMS, email, and even phone lines) at once.
The key strength is continuity. If a customer chats with your support bot on your site and comes back later via WhatsApp, the system remembers the earlier interaction. That context helps avoid repetition and reduces frustration.
These agents work best in businesses where users engage across channels and expect quick, personalized help each time.
To build them, you need strong backend integration, consistent training data, and a plan to manage user identity across platforms.
4. Functionality Comparison
The real difference between chatbot vs conversational AI comes down to what they can actually do in practice.
Below is a side-by-side look at their capabilities, especially in terms of automation, integration, and flexibility.
Chatbots
Handle FAQs, basic customer service, or order updates
Book appointments or capture leads using fixed logic
Operate 24/7 but follow a fixed set of rules
Often siloed, with minimal system integration
Conversational AI
Understand complex, multi-turn conversations
Automate workflows like onboarding, approval flows, or support escalations
Fetch and update live data from backend tools like CRMs or ERPs
Offer multilingual, cross-platform support
Escalate to human agents with full context when needed
As you explore the chatbot vs conversational AI differences, the choice depends on how deeply your system needs to understand, adapt, and automate customer interactions.
For many growing businesses, the right starting point is often a hybrid or phased rollout.
Read more: Check out top 10 voice ai agent development companies if your planning to build voice AI product.
Chatbot vs Conversational AI Common Use Cases
Once you understand the chatbot vs conversational AI differences, the next step is knowing where each fits best.
Here’s a breakdown of practical use cases we’ve seen across industries.
Chatbot Use Cases
Chatbots work best when speed and structure matter more than complexity. These use cases are ideal for startups or teams looking for efficient, rule-based automation.
1. Answering FAQs
Useful for quick responses to repetitive questions like business hours, return policies, or delivery timelines. Saves your support team from handling the same queries over and over.
2. Appointment or reservation booking
Often integrated into websites or mobile apps to let users book slots without waiting for human support. Works well for clinics, salons, or service businesses.
3. Order tracking or status updates
Customers can check the progress of their orders without needing to contact your team. Ideal for e-commerce and logistics platforms.
4. Lead capture via popups or forms
Chatbots on landing pages can collect user info, qualify leads, or route them to the right team, especially useful for SaaS and agency sites.
Conversational AI Use Cases
When the goal is deeper automation, personalized service, or complex task handling, conversational AI steps in.
These examples show how teams use it to scale both customer and internal operations.
1. Customer service automation
Handles full customer service flows, including multi-step queries like returns, complaints, or technical troubleshooting. Speeds up resolution and reduces agent workload.
2. Internal support (HR, IT, Ops)
Used inside companies to help employees reset passwords, apply for leave, or report issues. Cuts down internal ticket volumes.
3. Financial services
Delivers real-time account summaries, personalized investment advice, and supports secure banking transactions via apps or voice.
4. Post-purchase engagement
Manages returns, warranty queries, and product troubleshooting. Keeps users informed and reduces drop-offs after the sale.
5. Conversational commerce
Assists users in discovering products, comparing features, and even completing checkout, especially valuable for high-conversion D2C and retail brands.
Whether you’re building a simple chatbot for lead generation or a full conversational AI chatbot vs assistants platform for customer operations, the right use case can guide your roadmap.
Check out: Our AI voicebot development services to build voice bots for your business.
Advanced Capabilities and Applications of Conversational AI
Moving from basic chatbot scripts to intelligent automation isn’t just a tech upgrade. It’s a shift in how businesses handle support, onboard users, and drive engagement.
Conversational AI opens up new possibilities by combining natural language understanding, machine learning, and backend integration into a single system that can think, act, and adapt in real time.
Here’s what sets it apart:
1. Understands Intent, Sentiment, and Context
Conversational AI can go beyond keyword matching. It reads the user's message and understands what they’re really trying to do.
Whether the input is vague, emotional, or multi-layered, the system breaks it down into intent and sentiment.
It also remembers previous interactions, so users don’t need to repeat themselves across sessions.
This helps deliver answers that feel more natural, relevant, and less robotic.
2. Automates Complex Workflows
These systems are not limited to answering the questions but are capable of handling the whole task.
Whether it’s resetting passwords, checking eligibility, filing claims, or approving documents, conversational AI can handle multi-step flows without switching to a human agent.
It connects directly to backend tools like CRMs, ERPs, and ticketing systems. The result is faster resolution, fewer dropped queries, and more efficient internal teams.
3. Delivers Multilingual, Omnichannel Support
Today’s users expect help where they are, whether that’s inside a mobile app, on WhatsApp, or through voice.
Conversational AI can serve across all these channels while keeping the conversation consistent.
It understands and replies in multiple languages, adjusts to platform-specific UX, and carries context from one device or channel to another.
This reduces friction and improves support quality for global, mobile-first users.
4. Learns and Adapts Over Time
Every interaction feeds back into the system. Conversational AI uses this data to improve how it responds, what it suggests, and how it routes conversations.
If users are often confused at a certain step, the system can adjust its messaging. If a new product question comes up repeatedly, it learns to handle it without being manually updated.
This makes the system more reliable over time and reduces the need for constant tuning.
5. Drives Proactive and Personalized Engagement
It’s not just about waiting for the user to start a chat. Conversational AI can initiate relevant messages based on real-time triggers.
If someone abandons a cart, faces a billing issue, or qualifies for a feature update, the system can step in at the right time with the right message.
These touchpoints improve conversion, reduce churn, and keep users more engaged without manual intervention from your team.
6. Fits Across Verticals
This technology is already in use across industries with different needs.
In healthcare, AI systems help patients check symptoms, book appointments, and receive follow-up reminders—all synced with patient records.
In retail, they recommend products, check live stock, and manage returns.
In financial services, they support onboarding, detect fraud patterns, and explain account activity securely and clearly.
In SaaS, they guide onboarding, answer product queries, and triage support before it reaches the helpdesk.
These capabilities define the real difference between a basic chatbot and a truly conversational system.
If your business is dealing with growing user volume, complex processes, or expanding support needs, then conversational AI gives you the intelligence and flexibility to scale without compromising experience.
Choosing the Right Solution: Chatbot or Conversational AI?
By now, the chatbot vs conversational AI differences are clear.
But which one is right for your use case?
It comes down to your goals, user needs, and system complexity.
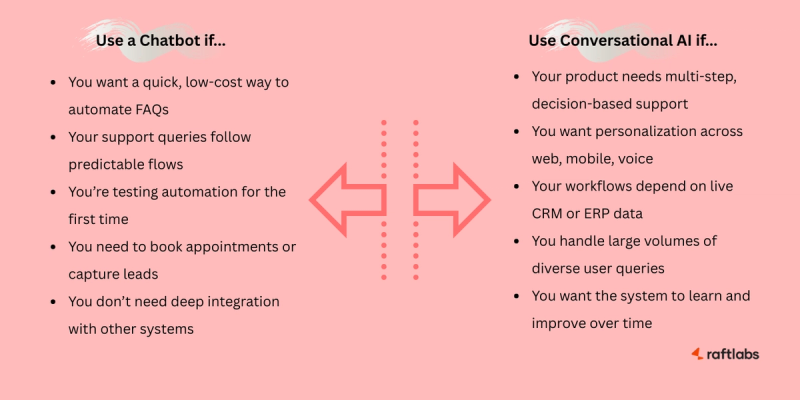
When to Use a Chatbot?
You need a quick and affordable way to automate FAQs or basic workflows
Your team is early in its automation journey and wants to test digital support channels
You want to capture leads, book appointments, or provide out-of-hours coverage without deep integrations
Your customer queries follow a predictable, structured pattern
You want full control over replies for compliance or brand safety reasons
Your use case is narrow, like tracking orders or routing users to the right page
Your team lacks in-house AI or data science expertise, so you want something simple to manage
You’re running short-term campaigns where speed of setup matters more than depth
When to Use Conversational AI?
Your product or service involves multi-step queries or decision-based interactions
You want users to get consistent, personalized responses across web, mobile, voice, and chat platforms
Your business depends on pulling or pushing data from internal systems like CRMs, ERPs, or inventory tools
You’re scaling and need a support system that can learn, adapt, and handle diverse queries at volume
Your support volume is growing faster than your team can scale
You offer services that involve user decision-making, like insurance, loans, or booking
You want to reduce agent fatigue by letting AI handle repetitive or Tier 1 queries
You’re offering personalized experiences for different user types, languages, or regions
If you're still evaluating, a hybrid approach works well, start small with a chatbot, then scale into conversational AI as your needs grow.
At RaftLabs, we help teams build both. Whether you need a basic bot or a fully integrated assistant, we can guide you through the decision and implementation.
When to Combine Chatbots With Conversational AI?
For many growing teams, the best solution isn’t choosing one over the other. It’s knowing when to combine them. A layered approach lets you balance cost, speed, and user experience.
1. Use chatbots as your first line of support
Start with a rule-based chatbot to handle common queries, guide users through menus, and route them efficiently. It’s a low-lift way to deflect basic tickets.
2. Let conversational AI step in when complexity rises
Once a user moves beyond FAQs or structured flows, escalate to conversational AI. This handoff ensures users get personalized, accurate help without hitting dead ends.
3. Blend automation with personalization
Chatbots deliver speed and scale. Conversational AI brings context and relevance. Together, they help you support more users while still offering a human-like experience when it matters.
4. Support phased implementation
Start with chatbots to launch quickly. Layer in conversational AI for selected workflows like onboarding, claims, or account support. This helps you validate value before scaling further.
5. Serve multiple user segments better
Use basic chatbots for general visitors, and conversational AI for logged-in users or high-value accounts needing deeper support, recommendations, or transactions.
This hybrid setup lets you unlock the full potential of both systems. Instead of choosing sides in the chatbot vs conversational AI debate, you build a flexible, future-proof support stack.
Is Conversational AI Replacing Chatbots?
The short answer is no. Conversational AI isn't replacing chatbots. It’s evolving from them and often building on top of them. Both still play valuable roles, depending on your business stage and customer needs.
1. Chatbots Remain the Starting Point for Many Teams
Early-stage businesses often begin with rule-based chatbots. They're fast to deploy, cost-effective, and useful for handling structured tasks like FAQs and lead capture.
2. Conversational AI builds on what Chatbots Started
As customer needs grow more complex, businesses upgrade by adding NLP, ML, and context awareness to existing chatbots—turning static flows into intelligent, adaptive systems.
3. Both Systems now Work Together in Layered Setups
In modern architectures, chatbots often act as the first filter. When conversations move beyond basic queries, conversational AI takes over to provide deeper engagement and smarter support.
4. You don’t have to Start from Scratch
Many platforms allow you to enhance your current chatbot with conversational AI features. No need to rebuild your entire stack. This makes scaling more practical and budget-friendly.
5. The Shift Reflects Changing Customer Expectations
Users now expect natural, personalized interactions across channels. While chatbots handle the basics, conversational AI delivers the kind of experience that keeps people engaged.
The best solutions are designed to grow with you, not lock you into one path.
How to Choose the Right One for Your Business
There’s no one-size-fits-all answer. What works for one product or team may not fit another. Here’s how to evaluate what fits your context best.
1. Map Your Customer Journey First
Begin by laying out all the key points where your users interact with your product or team. Look at what they ask, when they reach out, and what they expect.
If these interactions mostly follow a fixed pattern, like checking delivery status or updating profiles, a chatbot will handle them well.
But if users move through complex steps like booking with conditions or navigating multiple choices based on their history, you will need the deeper understanding and flexibility of conversational AI.
2. Consider Query Complexity and Intent Variety
Go through a sample of real user questions or support tickets. If you see a lot of “how do I” or “what if” type questions where the same question can mean different things depending on the context, you’ll want a system that understands nuance.
Chatbots are good for one-intent, one-response flows. Conversational AI gives you more freedom to guide a user when they don’t always know the right question to ask. It also handles corrections and follow-ups much better.
3. Check Your Integration Needs
Think about what actions the system needs to take. If users just need fixed answers or simple form fills, you don’t need to plug into anything deep.
But if the assistant needs to fetch real-time order data, check subscription status, or update user preferences in your CRM, you’ll want conversational AI.
It connects to multiple systems, sends and receives data, and turns conversations into actions. Without that, you may find chatbots hitting a wall too often.
4. Evaluate Support Volume and Team Size
When you’re handling thousands of queries daily or supporting users across time zones, languages, or product types, you need a system that can adapt without manual rule updates. Conversational AI is built for these kinds of use cases.
If your team is small and tickets are fewer or more uniform, a chatbot can give you relief without overengineering the solution. Start from the pain points your support team sees every week and build from there.
5. Start Small, Then Scale Smart
You don’t need to go all-in on day one. Many teams start with a basic chatbot to automate one or two key workflows like lead capture or booking.
From there, they analyze what works and what breaks. This helps validate the value of automation before investing in conversational AI.
Once you’ve proven that users are engaging and that deeper integration is worth the effort, then move toward more intelligent systems.
6. Factor in Total Cost of Ownership
Conversational AI has ongoing needs. It might reduce tickets or boost engagement, but it also needs regular monitoring, training data, updates to models, and performance tuning. You’ll likely need help from product, engineering, and data teams along the way.
A chatbot, on the other hand, has lower setup and maintenance costs. It’s more predictable but also more limited. Don’t just look at launch cost. Look at what it will take to run smoothly after month three.
7. Match Solution to Business Goals
If your focus is on lead generation, and you need a fast, frictionless way to qualify prospects and route them to your sales team, a chatbot might be enough.
But if your product requires hand-holding, education, or longer onboarding flows where every user path is different, conversational AI gives you more options to adapt.
Think about what success looks like for your business. Choose the system that helps you hit those numbers faster and with less manual effort.
Choosing between a conversational AI chatbot or a voice assistant setup depends on how you want to scale support, personalize engagement, and connect your systems.
At RaftLabs, We work with startups and enterprises by providing product discovery services to design the right fit, or if you’ve existing product we help you and make ready to scale intelligently.
Conversational AI Solutions Built by RaftLabs
We help startups and enterprises move beyond static forms and traditional workflows by building AI-driven systems that adapt to real user needs.
Here are two projects that show what that looks like in action.
1. SaaS Chatbot for Real-Time Product Feedback
We partnered with a SaaS startup to replace rigid surveys with live, conversational feedback flows. The system guided users through multi-step questions, captured structured input, and logged responses for instant analytics.
Built using React, WebSockets, and a multi-tenant PostgreSQL backend
Combined custom NLP logic with GPT-4 fallback for natural responses
Helped product managers uncover insights without relying on spreadsheets
This tool turned passive data collection into a two-way feedback engine.
2. Voice Chat App for Fast, Anonymous Decision-Making
PSi, a web app we built for internal voice-based collaboration, was designed to help distributed teams move faster without formal meetings or long threads.
Enabled real-time group discussions and anonymous voting
Delivered using Next.js, Hasura, and PostgreSQL for scalability
Replaced slow decision cycles with fast, inclusive conversations
Within 14 weeks, the platform helped the client scale engagement while reducing delays and meeting overhead.
These use cases show how we build conversational systems that are scalable, secure, and deeply aligned with business goals.
Conclusion
In 2025, both chatbots and conversational AI play critical roles in how businesses engage with customers, streamline operations, and scale support.
While chatbots offer a quick, affordable way to automate simple tasks, conversational AI enables more intelligent, personalized, and integrated interactions across channels.
Rather than viewing them as competing technologies, many teams are using them together, starting with a chatbot to handle routine flows and layering in conversational AI to manage complex, high-value use cases.
This blended approach helps improve user experience, reduce operational costs, and future-proof your support systems.
At RaftLabs, we help companies build automation that fits their real-world needs, whether you're launching a proof of concept or scaling enterprise workflows. We’re here to help you navigate the path from idea to impact.
FAQs
- Can I start with a chatbot and upgrade to conversational AI later?
Yes. Many of our clients begin with a simple chatbot to validate use cases and layer in conversational AI once they see traction or need deeper automation.
- How long does it take to build and launch a custom conversational AI solution?
A basic MVP can be delivered in 6–8 weeks. More advanced, integrated systems typically take 12–14 weeks, depending on scope, channels, and data access.
- Will AI tools integrate with our current tech stack (CRM, ERP, analytics)?
Absolutely. We design conversational systems to connect with tools like HubSpot, Salesforce, custom CRMs, and internal APIs, so your workflows stay smooth and data-rich.
- Is it possible to personalize conversations based on user behavior or history?
Yes. With the right backend integrations, AI can adapt responses based on past interactions, preferences, or user segments, just like a smart sales or support rep.
- What’s the ROI compared to hiring more support staff?
Conversational automation reduces repetitive workload, shortens response times, and handles volume spikes without extra headcount, resulting in better margins and scalable CX.
Insights from our team
let's talk about your project
Generative AI, voice AI, automation, SaaS — whatever you're building, we'll help you launch and stay with you long after.
We're not just another AI company chasing buzzwords. We design, build, and scale AI-powered products while standing behind every line of code.
Clients choose us not only for our expertise but because we stay available, communicate clearly, and treat their success as our own.


