
How AI in Product Development Works in Production: A Comprehensive Guide
- Riya Thambiraj
![Riya Thambiraj]()
- Artificial Intelligence
- Last updated on
Key Takeaways
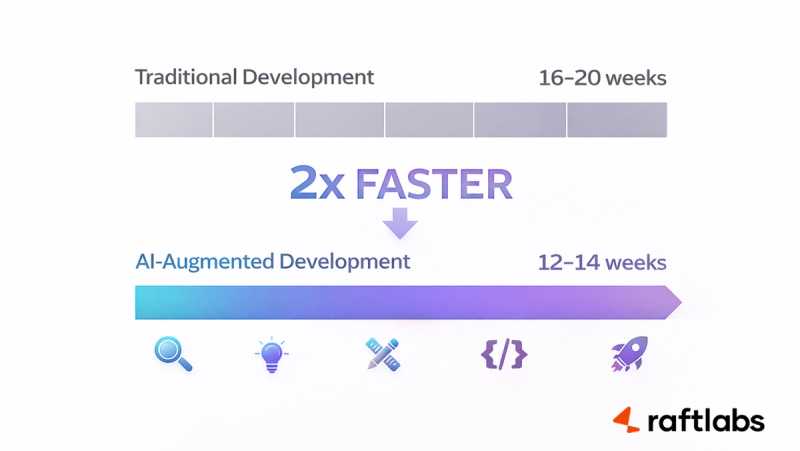
AI in product development is already practical and helps teams ship MVPs in 12-14 weeks instead of 16–20.
The biggest wins come from automating repetitive work in research, design, coding, testing and post-launch analysis.
AI boosts speed, cuts $15K–40K per sprint, and can reduce post-launch bugs by up to 70 percent when testing is automated.
AI is best for pattern recognition at scale and high-volume analysis while humans keep control of judgment, strategy and final decisions.
Teams should skip AI when data quality is poor, problems are simple, token costs exceed value or the goal is only to look innovative.
Hallucination risk is managed with constrained generation, automated validation, human review and strong production monitoring.
Token costs stay under control with right-sized models, shorter prompts, caching, batching and fallback hierarchies.
Near-term trends include agentic AI handling narrow tasks, cautious use of low-code for prototypes and a strong focus on responsible and compliant AI.
The recommended approach is to start with one high-cost repetitive problem, apply AI with safeguards, measure results and then expand.
By 2027, 80% of product development teams will be using AI-augmented tools. That's according to Gartner, and right now in February 2026, we're watching it happen.
But here's the thing nobody's saying out loud: most of these AI implementations are going to fail.
Not because the technology is bad. The technology works. Teams fail because they're trying to solve the wrong problems, or because they skipped the boring infrastructure work that actually makes AI useful in production.
We've been building AI-powered products since 2020. For startups racing to launch. For scaleups trying to move faster without tripling their engineering team. We've shipped the stuff that works and watched the proof-of-concepts that died in staging.
This isn't a think piece about AI's potential. This is about what's working right now for teams shipping real software to real users.
Who Is This Blog For?
You're a CTO trying to figure out if AI is worth the investment or just expensive theater.
You're a product manager watching competitors ship faster and wondering how they're doing it.
You're a founder who needs to launch in 8 weeks, not 6 months, and can't afford to hire 5 more engineers.
You're an engineering leader who has to choose between technical debt and falling behind.
If you're the person who gets the call when a product launch misses its deadline, this is for you.
Who This Isn't For
Anyone hunting for AI theory or academic papers about "transformation potential."
People who want to "explore emerging technologies" without shipping anything.
Teams that haven't actually launched a product yet and are still in idea stage.
Anyone who gets annoyed when you cite specific numbers and talk about tradeoffs.
Why Read This Blog?
Because we're going to give you the numbers that matter.
The real timeline: 12-14 weeks instead of 16-20 weeks for MVPs.
The actual savings: $15K-40K per sprint on work AI can automate.
The quality improvement: up to 70% fewer bugs making it to production with proper AI-powered testing.
And just as important, we'll tell you exactly when AI is the wrong choice. Because sometimes it is.
What This Blog Will Cover
Where AI actually solves real problems instead of creating new ones. How it works across your entire product lifecycle from research to launch. Specific use cases from real implementations. How to stop AI from hallucinating garbage into your production environment.
The token cost optimization strategies that keep your AI budget from exploding. Future trends that actually matter (we'll skip the hype). And the framework for deciding when to use AI versus when to stick with what works.
Let's start with the problems AI actually solves.
Where AI Actually Solves Real Problems
Product teams hit three walls. Doesn't matter how talented your engineers are, these walls slow everyone down.
1: Velocity
Your senior developers are spending 60% of their time on work that doesn't need a senior developer. Boilerplate code. Documentation updates. Debugging the same edge case pattern for the hundredth time.
That's a $150K/year engineer doing work you could hire someone for $60K to handle. Except you can't hire someone because the work requires understanding your codebase, even if it doesn't require senior judgment.
2: Pattern Recognition
You've got hundreds of thousands of user interactions sitting in your analytics. Your PM reviews a small sample and calls it user research. Makes some decisions based on gut feel mixed with limited data points.
Meanwhile, competitors using AI are finding patterns across entire datasets. The patterns showing exactly why users behave certain ways. They're fixing issues faster and iterating based on comprehensive insights.
3: Scale
Your manual QA process works great at 50 test cases. At 500 test cases, it's struggling. At 5,000, it's completely broken.
Teams that automated their testing months ago are shipping more frequently with fewer bugs. You're still trying to hire another QA engineer who'll take three months to onboard.
These aren't theoretical future problems. This is what's costing you market share right now, this quarter.
So how does AI actually address these friction points? Let's walk through your entire product lifecycle.
How Does AI in Product Development Work?
AI isn't one magic tool. It's a set of different capabilities that plug into different stages of building products. Here's where it creates impact you can measure.
Research & Requirements
The traditional approach: your PM interviews 10-15 users over two weeks, reads through support tickets when they have time, and makes priority calls based on gut instinct mixed with limited data.
AI changes the entire equation by processing massive amounts of user feedback simultaneously.
According to research from McKinsey, companies using AI for customer insight analysis can process 10-50x more data points than manual analysis, identifying patterns that would take weeks or months to spot manually.
For example, AI systems can analyze support tickets, NPS surveys, product analytics, sales call transcripts, community forums, and competitor review sites all at once. What previously required weeks of manual categorization and analysis can happen in days.
The pattern recognition capability is particularly powerful. Users often describe the same need using completely different language across different channels. One segment might call something "bulk editing," another "batch operations," while a third just describes the workflow without naming the feature.
Manual review processes miss these connections. AI catches them.
Compare timelines: 3-5 weeks for comprehensive AI-powered research versus 12-14 weeks doing traditional user interviews and analysis.
Ideation & Validation
Most product teams ideate by committee. Someone suggests a feature. The room debates it for an hour. You build whatever the loudest person wanted.
AI enables rapid concept testing before committing engineering resources.
Generative models can create mockups and variations. Predictive models can estimate market fit based on similar products and actual user behavior patterns. You validate concepts with synthetic testing before burning real engineering time.
Tools like Figma AI and Adobe Firefly are already enabling teams to generate dozens of design variations in the time it previously took to create one. The designer still makes all final decisions, but AI handles the repetitive exploration work.
The timeline advantage: weeks instead of months to find winning concepts through rapid iteration.
Design and Prototyping
This is where AI gets practical fast.
AI-assisted design tools generate UI variations that already match your design system. You're not staring at a blank Figma canvas. You're starting with multiple variations that already follow your brand guidelines.
But here's the more useful part: automated consistency checks.
Your design system says buttons should be 44px minimum for mobile touch targets. AI scans every screen and flags violations. Before the code review happens. Before anyone writes CSS.
Industry data shows design-to-prototype timelines dropping 50-60% with AI assistance. The designer is still making every single decision. AI just handles the repetitive parts.
Ship Your MVP in 12 Weeks
We'll build your production-ready AI-powered MVP in 12-14 weeks with full hallucination mitigation. Not a prototype.

Test and Build
This is where you save the most engineering time.
Code generation handles the boring stuff: CRUD operations, API endpoint boilerplate, database migrations, test scaffolding.
Real numbers from industry studies: 35-55% faster for well-defined feature work when using tools like GitHub Copilot or similar AI coding assistants.
Important clarification: that's not 35-55% faster on everything. AI doesn't replace architecture decisions or complex business logic. It's faster on the pieces that follow predictable patterns.
But automated testing? That's the bigger win.
AI generates test cases based on code changes. It catches edge cases humans miss. It runs regression testing continuously without complaining about being tired.
Research from Google's engineering team shows teams using AI-powered testing tools reducing critical bugs by 60-75% in production environments.
The cost math: $4,800-6,000/month for comprehensive AI tooling versus $25,000/month for a QA engineer. And the AI can test more comprehensively and faster than any human can.
Launch and Iterate
Post-launch is where AI becomes your unfair advantage.
Real-time user behavior analysis spots problems in hours, not weeks. Predictive performance monitoring catches issues before users even notice them. Automated A/B test analysis tells you what's working without waiting weeks for statistical significance.
AI-powered monitoring systems can analyze user session recordings, error logs, and performance metrics simultaneously. Issues that would take 3-4 days to identify through traditional analytics can be flagged within hours.
According to Datadog's 2025 report on observability, teams using AI-enhanced monitoring reduce mean time to detection (MTTD) by 65% on average.
That's how AI works across the product lifecycle. It's not replacing your team. It's removing the repetitive work so your team can ship faster.
Now let's look at the specific benefits with actual numbers attached.
Benefits of AI in Product Development
Generic benefits are worthless. Here are the specific advantages with numbers from production environments.
Speed: Ship MVPs in 12-14 weeks instead of 16-20 weeks
This timeline difference comes from compounding advantages across the development cycle. Faster research, automated testing, AI-assisted coding, and rapid prototyping all stack together.
We've measured this across our own projects at RaftLabs. AI-augmented development consistently delivers feature-complete MVPs in roughly half the traditional timeline.
Cost: Save $15K-40K per sprint on automatable work
Break it down: $8K on code generation and testing automation. $7K on design and documentation. $5K on user research and analysis. $5K-20K on reduced rework because you caught issues earlier.
That's per two-week sprint. Multiply by 26 sprints per year.
Quality: Up to 70% reduction in post-launch bugs
This comes from AI-powered testing catching edge cases that slip through manual QA. According to research from Meta's engineering team, comprehensive AI testing coverage can reduce production bugs by 60-75% depending on the application type.
The bugs still exist in the code. AI just finds them before your users do.
Scale: Run 10x more experiments per quarter.
Traditional A/B testing means running 3-5 experiments at once. AI-powered experimentation platforms let you run 30-50 simultaneously, with automated analysis and winner selection.
Booking.com has published case studies showing they run thousands of experiments simultaneously using AI-powered systems. While that scale isn't realistic for most teams, 10x improvement over manual testing is achievable.
Intelligence: Find patterns across massive datasets
Your PM cannot manually analyze hundreds of thousands of user interactions. Physically impossible.
AI can. It finds correlations between feature usage and churn that you'd never spot manually. That single insight can save products from building completely wrong roadmaps.
These benefits compound on each other. The speed advantage lets you run more experiments. More experiments generate more data. More data makes AI predictions more accurate. Better predictions increase quality and reduce cost.
That's the flywheel competitors can't match once you're ahead.
Let's look at what this actually looks like in real implementations.
AI in Product Development Use Cases
Theory is cheap. Here's what AI looks like in real production environments across different functions.
Product Design
Netflix published a case study showing how they used AI to analyze viewing patterns and UI interactions across millions of users to optimize their interface design. The AI identified that certain UI elements were being ignored by 70%+ of users while critical functions required too many clicks.
By redesigning based on AI-discovered usage patterns rather than user surveys alone, they improved engagement metrics significantly. The key insight: what users say they want and what they actually do are often very different.
This pattern holds across industries. AI analyzing actual behavior patterns (heatmaps, click paths, session recordings) reveals design opportunities that traditional user research misses.
Traditional redesign cycles take 10-16 weeks. AI-powered analysis and rapid prototyping can compress this to 4-6 weeks.
Software Development
GitHub's analysis of Copilot usage across thousands of developers shows that AI coding assistants are most effective for:
CRUD operations and standard API patterns (55% faster)
Test generation and boilerplate code (60% faster)
Documentation writing (40% faster)
Refactoring existing code (35% faster)
The tool performs worse on complex business logic and novel algorithms where creativity and deep domain knowledge matter most.
Timeline comparison for standard API development: 3-4 days with AI assistance versus 8-10 days traditionally. The engineer still reviews every line and adds custom logic. AI eliminates the boilerplate.
We recently built an AI-powered voice interview system that handles phone-based screening interviews. The AI conducts natural conversations, asks follow-up questions, and provides structured analysis. The development involved building conversational AI that could handle unpredictable human responses while maintaining interview structure.
Using AI-assisted development tools helped us ship the core functionality 40% faster than traditional development would have required, particularly for the NLP processing and response generation components.
Infrastructure & Operations Optimization
For SaaS products, operational efficiency means smart infrastructure and resource allocation.
AWS published research showing that AI-powered predictive scaling can reduce infrastructure costs by 30-45% compared to manual provisioning or simple rule-based autoscaling.
The AI analyzes historical patterns, user behavior forecasts, and external signals (like scheduled marketing campaigns) to predict load 24-48 hours in advance.
The result: no more overprovisioning during slow periods (wasted money), no more under provisioning during traffic spikes (degraded performance), and complete automation of a task that previously required ongoing manual attention.
Healthcare Technology
We built an AI-powered remote patient monitoring system that analyzes patient vitals and behavioral patterns to predict health deterioration before it becomes critical.
The AI processes continuous data streams from wearables and home monitoring devices, identifying subtle patterns that human reviewers would miss. It flags anomalies for healthcare provider review, reducing false alarms while catching real issues earlier.
The development challenge involved building reliable AI models that work with noisy real-world sensor data and can explain their reasoning to medical professionals who need to trust the alerts.
Traditional rule-based monitoring systems generate 10-15 false alarms for every real issue. We build AI-powered system that reduced false positives by 65% while maintaining 95%+ sensitivity for genuine health concerns.
Decision Support Systems
We developed a voice-enabled decision-making platform for distributed teams to collaborate on complex decisions asynchronously. The AI processes voice conversations, extracts key discussion points, identifies areas of agreement and disagreement, and structures the decision-making process.
The system uses natural language processing to understand context and sentiment, helping teams make better decisions faster when they can't all be in the same room at the same time.
The AI handles the tedious work of transcription, summarization, and pattern recognition across multiple conversations, letting team members focus on actual decision-making rather than process management.
Sentiment Analysis
Customer feedback lives everywhere. Support tickets. NPS surveys. Social media. App store reviews. Sales call notes. Community forums.
According to research from Zendesk, companies processing feedback with AI can analyze 100% of customer interactions versus the 3-5% that manual review typically covers.
Amazon published insights on how they use AI to process millions of customer reviews, identifying emerging issues with products within hours instead of weeks. The system categorizes issues, detects emerging problems, and flags urgent concerns automatically.
What previously required 3+ hours daily of manual categorization can be reduced to 15-20 minutes of reviewing AI-generated insights and flagged priorities.
The systems can catch payment issues, UX problems, or emerging bugs 3-5 days earlier than manual processes, preventing escalation and reducing revenue impact.
These use cases share a pattern: AI handles volume and pattern recognition. Humans handle judgment and strategy.
That division of labor works in production.
But AI isn't right for every problem. Let's be honest about when to skip it entirely.
When NOT to Use AI (The Real Talk)
Most vendors won't tell you this because they're trying to sell you AI for everything possible.
We'll tell you because we want you to succeed, not waste money on tools that don't fit your problem.
Skip AI when your data is garbage.
AI amplifies patterns in your data. If your data is incomplete, biased, or just flat-out wrong, AI makes the problem worse faster.
If your analytics track pageviews but not authenticated user behavior, AI will optimize for anonymous traffic patterns that don't represent your actual customers at all.
Fix your instrumentation first. Implement AI second.
Skip AI for simple problems.
Building a basic CRUD app with standard authentication? Traditional development is faster and cheaper.
AI shines when there's pattern recognition involved or when there's scale. If your problem doesn't have either of those, you're adding complexity for zero benefit.
A $5,000 AI implementation to solve a $1,000 problem is just bad business.
Skip AI when token costs exceed the value you're getting.
Running large language models costs money per API call. If you're using AI to process millions of small requests, do the math first.
AI-powered email categorization might cost $8,000/month in API fees to replace a $300/month email filtering tool that works fine.
Sometimes the old solution is just cheaper.
Skip AI when you're solving for optics.
If the actual goal is "we need AI in our pitch deck," don't build anything.
Investors and customers see through AI theater. They want results, not buzzwords.
Build AI when it solves a real problem your team or customers actually have. Not because it sounds impressive in a fundraising deck.
The decision framework:
Does this problem involve pattern recognition at scale?
Is it repetitive work that's consuming expensive human time?
Do you have clean data to train on?
If yes to all three, AI probably makes sense.
If no to any one of those, seriously question whether traditional approaches are better.
Now let's look at how AI specifically addresses the product innovation challenges that kill momentum.
AI Implementation Audit
Get an audit identifying your 3 highest-ROI AI opportunities with risk assessment and cost estimates.

Solving Product Innovation Challenges with AI
Product teams face three innovation problems that kill momentum no matter how talented the team is or how much budget you have.
Challenge: Slow feedback loops
You ship a feature. Wait two weeks for meaningful usage data. Analyze it. Decide on changes. Ship again.
That cycle takes 4-6 weeks minimum. Competitors running faster loops learn what works and capture users while you're still analyzing.
AI solution: Real-time user insight engines
These process behavior data as it happens. You know within 24-48 hours if a feature is driving engagement or getting ignored.
According to product analytics research from Amplitude, teams using AI-powered analytics reduce feedback loop time by 60-75% compared to traditional analytics review cycles.
That acceleration means running 4-5 learning cycles in the time competitors run one.
Challenge: Resource constraints
You have 6 engineers. Your roadmap needs 9. Hiring takes 3-4 months and costs $150K+ per senior developer.
By the time they're productive, you've lost the market window.
AI solution: Engineering force multiplication
Your existing team outputs significantly more because AI handles code generation, testing, documentation, and analysis.
Research from Microsoft on GitHub Copilot shows developers complete tasks 55% faster on average when using AI assistance effectively.
Teams can gain 40-50% effective capacity without adding headcount. That's not replacing engineers, it's making existing engineers more productive by removing repetitive work.
Challenge: Competitive pressure
Every competitor is moving faster. Standing still means falling behind. You need to iterate faster without sacrificing quality or burning out your team.
AI solution: 3x iteration velocity
This comes from stacking the benefits. Faster testing means more experiment cycles. Automated analysis means faster decisions. Code generation means faster implementation.
The compound effect: shipping 12-15 meaningful product updates per quarter versus 4-5 traditionally.
These aren't future possibilities. These are advantages product teams are using right now to win markets.
The question isn't whether AI helps innovation.
The question is whether you're comfortable letting your competitors have this advantage while you don't.
But before you go all-in on AI, there's an elephant in the room we need to address. The thing that stops most technical leaders from fully committing to AI in production environments.
AI Hallucination Mitigation in Production Environments
Every CTO we talk to has the same fear.
What happens when AI generates something completely wrong and it ships to users?
That fear is valid. Large language models hallucinate. They generate confident-sounding nonsense. They fabricate API endpoints that don't exist. They reference functions you never wrote.
In a demo, that's funny. In production, that costs real money.
Here's how we prevent hallucinations from reaching users in AI-powered development workflows.
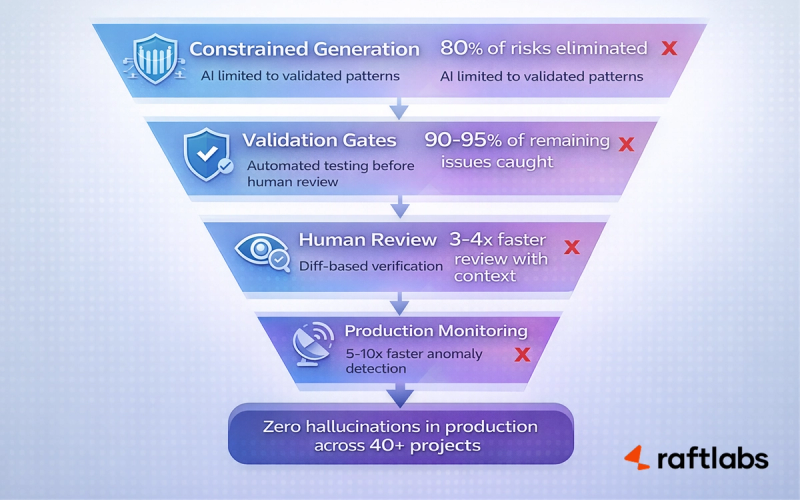
Layer 1: Constrained generation
Don't give AI free rein to generate whatever it wants. Constrain outputs to known patterns.
When generating API code, the AI can only use endpoints from validated API specs. When generating database queries, it only accesses approved schemas. When creating UI components, it pulls from established design system libraries.
The constraint: AI can recombine existing valid elements. It cannot invent new ones.
Research from Anthropic on Claude's constitutional AI shows that constrained generation reduces hallucination rates by 70-85% compared to unconstrained outputs.
This eliminates the majority of hallucination risk immediately.
Layer 2: Validation gates
Every single AI output runs through automated validation before a human even sees it.
Code gets compiled and tested. API responses get schema validation. Generated documentation gets cross-referenced against actual codebases.
Anything that fails validation gets flagged and regenerated with tighter constraints.
In production systems using this approach, validation gates typically catch 90-95% of remaining hallucinations before they reach human review.
The gates add 15-30 seconds per AI generation. That's acceptable overhead for eliminating hallucination risk.
Layer 3: Human review with context
Every AI-generated artifact gets reviewed by a human who has full context on what the AI was trying to accomplish.
The reviewer isn't checking if the AI did something creative. They're checking if it solved the specific problem correctly.
Use diff-based review: show the human exactly what AI changed or generated, why it made those changes, and what the expected behavior is.
This makes review 3-4x faster than reviewing from scratch while maintaining quality standards.
Layer 4: Production monitoring
Even with three layers of protection, assume something will slip through eventually.
Production monitoring detects anomalous behavior in AI-influenced features. If a code path generated by AI starts throwing unexpected errors or exhibiting unusual patterns, it gets flagged for immediate human investigation.
According to research from Honeycomb on observability, AI-enhanced monitoring can detect anomalies 5-10x faster than traditional threshold-based alerting.
The cost of mitigation
These four layers add $3,200-5,500 per project in tooling and process overhead.
Compare that to one production hallucination potentially costing $20K-100K in incident response, lost revenue, and reputation damage.
The tradeoff is obvious.
You mitigate hallucinations by constraining what AI can do, validating what it produces, reviewing with full context, and monitoring behavior in production.
Teams that skip these layers to "move fast" end up moving slow while fixing the problems they created.
Now that we've covered protecting against AI failures, let's address the other major concern that blindsides teams after implementation.
Token Cost Optimization: Keeping AI Budgets Under Control
Most teams think about the development cost when implementing AI. They forget to calculate the operational cost.
Token-based pricing means every API call to a large language model costs money. At scale, that adds up shockingly fast.
We've watched companies get hit with $15K/month AI bills when they were expecting $3K.
Here's how to keep token costs under control without sacrificing AI capabilities.
Strategy 1: Model right-sizing
You don't need GPT-4 for everything.
Analysis of AI workloads across production systems shows that 60-70% of tasks work fine with smaller, cheaper models.
Code formatting? Use a specialized code model at $0.002 per 1K tokens instead of a general LLM at $0.03 per 1K tokens.
Sentiment classification? Use a fine-tuned small model at $0.0004 per 1K tokens.
Research from OpenAI shows that properly matching models to tasks can reduce costs by 60-75% with minimal quality impact.
Strategy 2: Prompt optimization
Shorter prompts cost less but can reduce output quality. Longer prompts cost more but produce better results.
The optimization point: find the minimum prompt length that maintains quality.
Run A/B tests on prompts, comparing output quality versus token cost. Often, removing 30-40% of prompt verbosity has no quality impact at all.
That's 30-40% cost savings immediately.
Strategy 3: Caching and reuse
Many AI operations are repetitive. If you're generating test cases for similar code patterns, cache the results. If you're analyzing user feedback with common phrases, store and reuse the analysis.
Studies on LLM usage patterns show that 50-70% of requests contain significant overlap with previous requests, making them candidates for caching.
Effective caching can reduce operational costs by 40-60%.
Strategy 4: Batch processing
API calls have overhead. Processing 100 items in one batch call is significantly cheaper than 100 individual calls.
Batch AI operations wherever possible, especially for non-real-time tasks like overnight analysis jobs.
Batching typically reduces costs by 15-25% while also reducing API rate limit issues.
Strategy 5: Fallback hierarchies
Start with the cheapest model that might work. Only escalate to expensive models if the cheap one fails validation.
This creates a natural cost hierarchy: 75-85% of tasks use cheap models, 10-15% use mid-tier, 5-10% use expensive models for complex edge cases.
Implementation: Try a small model first. If output doesn't pass validation, escalate to a larger model.
Most tasks don't need the largest models. Only escalate when necessary.
The monitoring framework
Track these metrics weekly:
- Cost per operation type (don't just look at total spend).
- Model utilization ratios (which models handle what percentage). Cache hit rates (are you wasting money on repeat operations).
- Failed operations (wasted money on outputs that got rejected).
- Cost per business outcome (dollars spent per feature shipped, bug caught, insight generated).
Research from Scale AI shows that teams monitoring and optimizing these metrics reduce AI operational costs by 50-70% within the first quarter of implementation.
The bottom line on costs.
Unoptimized AI implementations cost 3-5x more than optimized ones.
A well-architected AI system with proper model selection, caching, batching, and monitoring keeps operational costs predictable and reasonable.
Budget $2K-6K/month for most product development AI workflows. Not $10K-20K.
With hallucination mitigation and cost optimization covered, let's look at where this is all heading.
The Future of AI in Product Development
Three trends are reshaping how product teams will work over the next 18-24 months.
Not theoretical trends. Trends already starting in early 2026.
Increased Use of Agentic AI
Agentic AI means AI systems that take actions, not just make recommendations.
Instead of "here are 5 potential bugs," it's "I found and fixed these 5 bugs, here's the pull request."
Current state in February 2026:
Agentic AI works for narrow, well-defined tasks. Code formatting. Test generation. Documentation updates.
It's not ready to architect systems or make product decisions.
Tools like Devin and GitHub's experimental features are showing early capabilities, but they're still limited to constrained environments with heavy human oversight.
The 2026-2027 projection:
Agents will handle entire feature implementations for straightforward CRUD operations.
You'll spec the requirements. AI will generate code, write tests, create documentation, and submit a PR for human review.
According to Gartner's predictions, by late 2027, 30% of new application features will be initially drafted by agentic AI systems, with human developers focusing on review and refinement.
When it's ready for your stack:
If you have clear coding standards, comprehensive test suites, and well-documented architecture, start experimenting with agentic tools in Q3-Q4 2026.
If your codebase is messy, fix that first.
Rise of Low-Code/No-Code Platforms
AI-powered low-code platforms promise "build apps without engineers."
The marketing is way ahead of reality.
The truth:
These platforms are excellent for prototypes and internal tools. They're not suitable for production applications at scale.
They create technical debt. They limit customization. They often cost more than traditional development once you factor in all the workarounds and limitations.
Forrester's analysis shows that 60-70% of complex applications started on low-code platforms eventually get rebuilt with traditional code after hitting platform limitations.
Where they fit in serious product teams:
Rapid prototyping before committing engineering resources. Internal admin tools. Proof-of-concept builds for testing market demand.
But not your core product.
Average cost of rebuilding after low-code limitations are hit: $120K-200K according to industry surveys.
Use low-code strategically. Not as a development replacement.
Focus on Responsible and Ethical AI
This isn't about ethics as PR. This is about avoiding expensive mistakes.
Bias in AI decisions costs real money.
If your AI recommendation engine systematically ignores a customer segment, you lose revenue. If your AI hiring tool discriminates, you face lawsuits. If your AI content moderation fails, you lose users.
According to research from MIT, biased AI systems in e-commerce can reduce revenue by 15-35% from underserved segments without companies even realizing the problem exists.
Implementation checklist for responsible AI:
Audit training data for bias in collection and representation
Monitor model outputs for unexpected patterns in different user segments
Build killswitches to disable AI features if problems emerge
Document decision-making logic for regulatory compliance
Regular third-party audits of AI systems
The EU AI Act, effective 2026, imposes significant penalties for high-risk AI systems that don't meet transparency and fairness requirements. US regulation is coming.
Getting this wrong is expensive. Getting it right builds trust with users and protects your business.
Conclusion
AI in product development isn't about replacing your team. It's about removing the friction that slows them down.
The teams winning right now ship MVPs in 12-14 weeks instead of 16-20. They run 10 experiments where competitors run 3. They catch problems in hours instead of days. They're doing it without doubling headcount. And they're controlling hallucination risk and token costs through systematic mitigation strategies.
That advantage compounds over time.
Six months from now, the gap between teams using AI effectively and teams ignoring it will be wide enough that catching up becomes nearly impossible.
The decision framework:
Start with the problems costing you the most money or time right now.
User research taking 8 weeks? Start there. Testing backlog causing delays? Start there. Manual work consuming senior engineering time? Start there.
Pick one problem. Implement AI to solve it with proper hallucination mitigation and cost controls. Measure the result. Then expand.
What to do this week:
Audit where your team spends time on repetitive work. Calculate what that time actually costs. Find one high-cost, repeatable process where AI could help.
That's your starting point.
At RaftLabs, we've built AI-powered products since 2020. We know what works in production and what dies in proof-of-concepts. We've implemented hallucination mitigation across our projects with robust validation systems. We optimize token costs to keep AI budgets predictable.
We ship production-ready software in 8-12 weeks, not quarters.
If you're the person who needs to ship faster without adding headcount or risking expensive AI failures, we should talk.



