
Conversational AI in Healthcare: Key Use Cases, Benefits & Future Trends
- Riya Thambiraj
![Riya Thambiraj]()
- Artificial Intelligence
- Last updated on
The healthcare industry is at a turning point. As patients demand faster, smarter, and more personalized experiences, healthcare providers are rethinking how they deliver care. This is where conversational AI in healthcare is making its mark.
From AI-powered chatbots answering patient queries to voice assistants helping clinicians streamline workflows, conversational AI technology in healthcare is a strategic advantage.
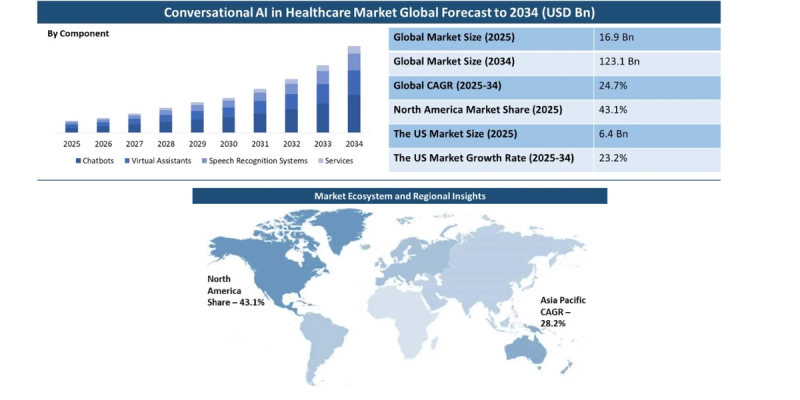
Source: dimensionmarketresearch.com
The global market for conversational AI in healthcare is set to reach $16.9 billion by 2025 and grow rapidly to $123.1 billion by 2034. For founders and product teams, this shows how fast the space is scaling and why moving early matters.
This surge is driven by a simple reality: healthcare systems need scalable, on-demand digital touchpoints to keep up.
Whether it’s automating appointment scheduling, simplifying medical billing, or enabling 24/7 virtual care, conversational AI use cases in healthcare are proving their value across the ecosystem.
Who Is This Blog For?
This guide is for:
Founders and co-founders exploring conversational AI in healthcare to improve patient care or streamline operations
Product managers and VPs planning AI features for onboarding, support, or clinical workflows
Agencies and CX leads helping healthcare brands handle queries at scale
Lean teams in hospitals, labs, or pharma aiming to scale support without hiring more staff
Enterprises experimenting with voice-first UX for kiosks, apps, or telehealth platforms
Anyone asking: How do we build a chatbot or voice assistant that patients and clinicians actually use?
Why Read This Blog?
Building a chatbot or virtual assistant for healthcare is more than picking the right tool.
It’s about solving real problems like faster triage, better patient engagement, seamless scheduling, without drowning in jargon or endless vendor demos.
At RaftLabs, we’ve helped:
Startups launch AI MVPs on tight timelines and budgets
Enterprises scale virtual assistants to handle conversations and voice feedback.
Teams stuck with half-baked ideas turn them into production-ready AI solutions
By 2026, conversational AI in healthcare and pharma will touch nearly every workflow, from front-desk queries to clinical decision support. The question isn’t if you need it. It’s how fast you can deploy and scale it effectively.
What This Blog Will Cover:
What conversational AI is and how it fits into healthcare
Core technologies powering chatbots and voice assistants
Benefits and use cases of conversational AI in healthcare
Development timelines, costs, and what to plan for
Challenges unique to healthcare AI and how to solve them
Lessons we’ve learned building healthcare AI apps
Before diving into implementation, let’s explore what conversational AI in healthcare really means and why it’s becoming a priority for startups and enterprises alike.
What is Conversational AI?
In healthcare, conversational AI helps you talk to patients and staff without manual effort. These aren’t the old bots that give static replies. They process language in real time and reply in ways that feel human, on chat or voice calls.
The difference between conversational or voice bots and old-school chatbots is massive.
They’re built on NLP, ML, and context tracking so they can manage multi-step conversations. From symptom triage to booking to pulling patient data; chatbots perform all these processes efficiently without the help of any humans.
With conversational AI, founders and product leads can shrink wait times, boost patient experience, and scale without adding headcount. One single interface does what used to need a stack of different tools.
Key building blocks of conversational AI
To design conversational AI that works in real healthcare environments, you need more than a chatbot UI.
It requires a set of core components working together like understanding patient intent, managing context, integrating with systems, and delivering a seamless experience across channels.
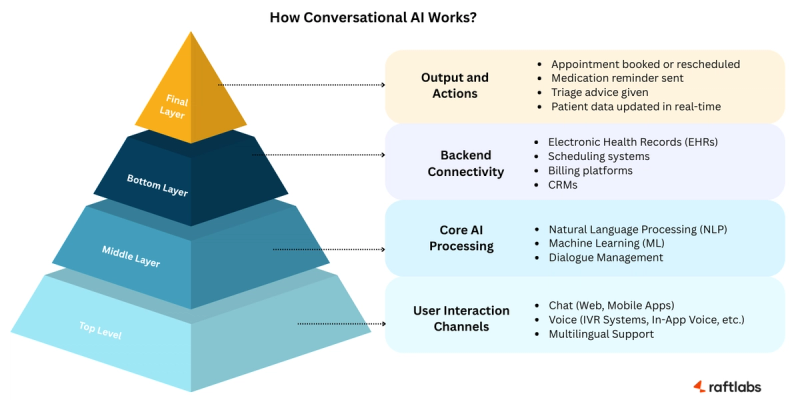
Here’s what goes into building a robust solution.
NLP
Understands how people actually talk. It can handle incomplete sentences, slang, or medical terms without getting lost.
Machine learning
Learns from every interaction. The system gets better at understanding intent and delivering accurate responses over time.
Dialogue management
Keeps the conversation flowing, even across multiple questions and topics, without making users repeat themselves.
System integration
Plugs into your existing systems like EHRs, schedulers, billing, and CRMs, to work with live data in real time.
Voice capabilities
Lets patients and clinicians interact hands-free, which is especially useful in high-pressure or accessibility-focused scenarios.
For healthcare and pharma leaders, conversational AI isn’t just a tech upgrade. It’s a way to solve operational bottlenecks, engage patients at scale, and free up staff for higher-value work.
Chatbots vs Conversational AI
Not every bot works the same way. Before we dive into conversational AI in healthcare, let’s see how it stacks up against basic chatbots.
This quick breakdown shows the big differences between chatbot vs conversational AI that matter in real-world setups.
| Feature | Chatbots | Conversational AI |
|---|---|---|
| Task Complexity | Simple, rule-based | Handles complex, nuanced queries |
| Language | Keyword-driven | Context-aware, understands intent |
| Interaction | Scripted, linear | Dynamic, human-like, multi-turn |
| Personalization | Limited | Highly personalized |
| Learning | Static | Learns and adapts over time |
| Integration | Basic | Deep backend and EHR integration |
This is why many healthcare teams are moving beyond rule-based chatbots.
Conversational AI offers the flexibility, intelligence, and integration needed to handle complex workflows and deliver patient experiences that feel natural.
Top Use Cases of Conversational AI in Healthcare
If you’re serious about improving patient experience and cutting operational drag, this is where conversational AI in healthcare software development industry is proving its value. These aren’t future ideas. They’re already working in real setups.
1. Appointment Scheduling and Reminders
AI can take care of most scheduling tasks that front-desk staff usually handle. Patients can book or cancel appointments by chatting or speaking with a bot.
They also get reminders before their appointment, which helps them show up on time. If they need to reschedule, they can do that easily without making a phone call.
Clinics that use this system have seen a big drop in no-shows. It also frees up phone lines and admin time.
2. Symptom Checking and Triage
This one works like a smart front line. Patients talk to a virtual assistant that asks about symptoms and tries to understand what’s going on.
Based on how serious the symptoms are, the AI can recommend whether they should go to the ER, book a consult, or manage at home.
It doesn’t replace a doctor, but it helps direct people quickly and avoid unnecessary wait times. Many clinics use this as a filter before assigning human resources.
3. Medication Management
Patients often forget to take medicines on time or miss doses altogether. Conversational AI can send reminders based on their prescription schedule.
Some systems also allow patients to confirm when they’ve taken the dose, which helps with adherence tracking.
If a refill is needed, the bot can send a reminder or even help trigger the refill process. This is helpful for chronic disease management and elder care especially.
4. Lab results and Test Notifications
Patients often feel anxious waiting for lab test results. AI can notify them instantly once the reports are available.
It can also explain what the result means in simple language or point them to a doctor if something looks abnormal.
This reduces the burden on doctors and support teams, who otherwise spend time answering repetitive status calls.
5. Post-Treatment Follow-Up
After a procedure or hospital discharge, a bot can check in with patients regularly. It can ask questions like how they are feeling, whether they are taking medicines properly, or if they have any side effects.
If any red flag shows up, the system can alert a nurse or doctor. This helps reduce readmission chances and keeps patients more connected to care without having to call every day.
6. 24/7 Remote Monitoring
When patients use wearables or home health devices, the data they generate often goes nowhere unless someone manually checks it. AI can connect to these devices and monitor the data in real time.
If something unusual is detected, like a sudden drop in oxygen levels or blood pressure spike, it can alert the care team immediately. This type of passive monitoring works well for high-risk or elderly patients who live alone.
7. Patient Onboarding and Education
When someone joins a new hospital or starts using a digital health app, there are always many small questions.
Conversational AI can help with filling forms, verifying insurance, explaining policies, and answering common questions about services.
It reduces friction and keeps patients from feeling lost in the system. It also allows staff to focus on higher-priority work.
8. Mental Health Check-Ins
Not everyone is ready to talk to a human therapist right away. AI bots can check in with users, offer support, and ask how they are doing emotionally.
If someone types something concerning, the system can flag it for a counselor.
This is not a replacement for care, but a good first step. Some therapists also use bots to handle reminders, journaling prompts, or basic triage.
9. Clinical Workflow Automation
Doctors and nurses lose a lot of time on admin tasks. Conversational AI can help them look up patient data, dictate notes, or send lab orders using voice or chat.
For support teams, the same system can be used to handle intake forms, verify insurance info, or respond to internal queries. It creates a smoother workflow and reduces clicks, delays, and human error.
10. Chronic Disease Management
For conditions like diabetes, hypertension, or asthma, AI bots can send daily check-ins, collect self-reported symptoms, and provide reminders.
The system can track patterns and alert care teams if something looks wrong, this gives patients the feeling of being supported without needing daily visits. It also gives providers a scalable way to manage a large population.
11. Preventive Care Nudges
Many people miss important health checks simply because they forget or don’t know they are due.
Conversational AI can keep track of age, history, and guidelines to nudge patients about screenings, vaccines, or regular blood tests.
These reminders can be sent via WhatsApp, SMS, or voice depending on the patient’s comfort level.
12. Health Education and Awareness
Instead of handing out printed brochures or long documents, AI can deliver personalized health information based on the patient’s condition, age, and history.
It can break down complex topics like cholesterol or blood sugar in plain language. If a patient has a question, they can ask follow-up queries in real time. This improves engagement and helps patients feel more in control.
13. Insurance and Billing Support
Healthcare billing is confusing. Conversational AI can walk patients through bills, explain insurance coverage, or help with filing claims. They don’t have to wait on hold or get bounced between departments. This saves a lot of support time and improves the overall experience.
14. Patient Feedback Collection
After a visit, patients often skip giving feedback because the process is slow. AI bots can ask for a quick rating or short message and collect input in real time.
The data can be shared instantly with the operations team to spot issues and fix them early. It’s faster and more reliable than traditional surveys.
Hospitals and startups are already using conversational AI to scale care, cut admin overhead, and give patients 24/7 access without overloading teams. The teams moving early are already ahead of the curve.
Hospitals and startups are already using conversational AI to scale care, cut admin overhead, and give patients 24/7 access without overloading teams. The teams moving early are already ahead of the curve.
Key Benefits of Conversational AI in Healthcare
Adopting conversational AI in healthcare goes beyond automating replies. It solves real problems for providers and patients, helping organizations deliver care faster, smarter, and at scale.
For Healthcare Providers
1. Streamline Operations
Most healthcare staff lose time doing the same basic tasks, appointment bookings, triage, and follow-up calls. AI handles these with no back-and-forth. It connects with calendars, finds slots, sends reminders, and even adjusts schedules when patients cancel.
Medbelle saw a 60 % rise in scheduling efficiency after launching conversational AI for appointment booking and reminders.
2. 24/7 Patient Support
Patients ask questions at odd hours. But teams can’t always reply late at night or during weekends. AI helps here. It answers FAQs, checks symptoms, explains procedures, and guides them on next steps, even at midnight.
Cleveland Clinic and Kaiser Permanente introduced AI scheduling and chronic-care bots, easing care access and shortening response times.
3. Better Diagnostics Support
AI doesn't replace doctors, but it helps them make faster calls. It listens to symptoms, checks for patterns, and offers support tools for triage. Nurses or staff can use it as a first filter before routing the patient.
The AIDA diabetes assistant handles symptom triage via text or voice, assisting patients and reducing clinician burden.
4. Scale Patient Communication
One human can’t reply to 500 patients in a day. AI can. It manages chat, voice, and email queries at scale. No one gets ignored. Everyone gets a reply fast.
Sword Health uses AI-powered messaging to boost physical therapist caseloads from ~250 to 700 patients per provider
5. Cut Operational Costs
Fewer manual tasks mean fewer people are needed to perform them. AI reduces the dependency on large support teams. There's less data entry and fewer phone calls, with more automation across the board.
UiPath’s AI system processed 100 million transactions annually for Omega Healthcare, saving 15,000 employee hours per month and reducing documentation time by 40 %.
6. Improve Data Capture
Patient conversations often get lost unless someone notes them down. AI records chats, transcribes voice inputs, and tags them for later use. This turns raw interactions into structured records.
Colorado-based telehealth company livepro installs “Luna,” a voice bot that automates contact center queries and supports multilingual patient interactions
7. Reduce Burnout
Admin load is one of the biggest reasons for staff burnout. AI takes care of common tasks like form filling, pre-visit questionnaires, and insurance verification. It keeps the human team focused on real care.
About 46 percent of doctors on Sermo said AI helped most by offloading boring, repeatable admin work.
8. Speed Up Decision-Making
Doctors often waste time hunting for info. AI can surface relevant patient history, lab results, or protocols during a consult. No need to click 10 tabs or call the front desk.
When decisions happen faster, patient wait time drops and care delivery improves across the board.
For Patients
1. On-Demand Access to Care
Patients don’t like waiting. AI gives them a way to ask questions or get care help instantly. Whether it’s 3pm or 3am, they get an answer.
Lark Health’s AI nurse interacts via text with over 1.5 million patients, offering advice on chronic conditions 24/7.
2. Faster Service
Booking appointments, asking about test results, or getting symptom advice shouldn’t take days. With AI, it doesn’t. Patients skip long calls and just get what they need right away.
Medbelle’s AI chatbot reduced no-shows and streamlined booking, dramatically reducing admin bottlenecks.
3. Personalized Care
AI tracks your condition, medication, and history. Then it gives advice that fits you, not just general info. It might nudge you about your diabetes meds or explain test results in simple words.
UpDoc’s voice-based insulin assistant helped 81 % of users maintain their glucose levels, compared to just 25 % in control groups.
4. Remote Monitoring Made Easy
You don’t need to visit a clinic for every check-in. AI connects with wearables or asks symptom questions over chat. It watches for red flags and alerts care teams when needed.
A voice-based triage system for older adults detected early-onset Type 2 diabetes through home conversations with 70 % accuracy.
5. Simpler Access to Records
Patients often struggle to understand or retrieve their reports. AI simplifies this. You ask a question, and it finds and explains the info without needing to log into five different portals.
Livepro’s Luna also provides real-time updates from approved knowledge bases, cutting staff workload and helping patients get quick answers livepro.com.
6. Improved Accessibility
Not everyone is tech-savvy. Some struggle with reading, others with language. AI helps bridge this gap. It talks in simple language, supports translations, and adapts to the user’s pace.
Most physicians reported a highly positive experience with AI scribes.
By integrating conversational AI technology in healthcare, founders and product teams can deliver smarter, more efficient care.
7. Better Health Decisions
AI doesn’t just share info. It helps people act. Whether it's choosing a glucose meter or signing up for a screening, AI guides them based on their profile and needs.
Smart assistants now recommend medical products or services in plain English and help users pick what fits their condition.
8. More Proactive Care
AI keeps a patient on track. It reminds them about upcoming checkups, vaccinations, or tests based on their history. This helps avoid missed steps and encourages preventive care.
Clinics using proactive AI reminders report higher screening rates and better patient follow-through.
How to Implement Conversational AI for Your Healthcare Platform
Rolling out conversational AI isn’t about adding a chatbot widget. You need to design for real-world workflows, patient expectations, and backend complexity.
Below is a step-by-step breakdown to help you get it right the first time.
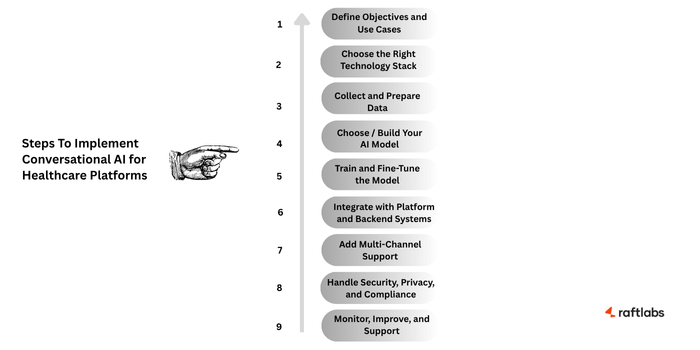
1. Define Objectives and Use Cases
Start with a simple question; what’s the one problem this bot should solve firs?.
Is it helping patients book appointments, do symptom triage, or answer insurance queries?
Try to be specific. If you try to solve everything at once, the outcome often falls flat. Pick 1–2 use cases where the value is clear and the workflows are known. That’s your foundation. You can expand later once the core flow works well.
2. Choose the Right Technology Stack
The stack you choose matters. You’ll need something that handles healthcare-specific language, scales with usage, and plays well with your existing backend.
Tools like Rasa, Google Dialogflow, or even custom LLM-based stacks can work. What you pick depends on the use case, team skill, and how much control you need.
Also, double-check if the stack supports HIPAA-level privacy and works with your authentication model.
3. Collect and Prepare the Right Data
Use real-world data if you want the model to perform well. This means pulling past chat logs, patient queries, and support transcripts. Remove anything irrelevant.
Clean it up and also tag the intents. This step takes time, but if your data is bad or inconsistent, your bot will keep giving broken answers.
In some cases, use synthetic data to fill gaps, especially for rare scenarios.
4. Choose or Build Your AI Model
You can either train your own model or start with something pre-built. If speed is important, start with Dialogflow, Azure Bot Framework, or an LLM-based tool like Cohere or Claude.
If you need tighter control and more security, build your own using open-source frameworks.
Custom models are better when your flows are highly domain-specific or when you're dealing with critical patient data.
5. Train and Fine-Tune the Model
Once the model is set, train it using your cleaned dataset. Then test how it performs. Don’t just check if it replies, look at how it handles messy input, slang, or medical terms.
Expect to go through multiple tuning rounds. Keep testing with real user input, not just perfect sample data.
Over time, the model should get smarter with more examples.
6. Integrate with Your Platform and Backend Systems
The bot is not useful unless it’s wired into your workflows. It should connect with your EHR, scheduler, billing system, or CRM.
That way, it can actually perform tasks like booking an appointment or pulling test results. Think of it as a layer that talks to users and executes actions in your system without human handoff.
Work with your dev team early to design how APIs and auth will be managed.
7. Add Multi-Channel Support If Needed
If your users interact on different platforms, the bot should be there too. Web, app, voice, maybe even WhatsApp or IVR.
But don’t launch everywhere at once. Start with your primary channel. Once that’s stable, extend to others.
Just make sure the experience is consistent and the backend logic remains the same, no matter which channel the user comes from.
8. Handle Security, Privacy, and Compliance
Healthcare data is sensitive. Every part of your system, from the NLP engine to your storage, must meet security standards.
Use encryption, enforce proper session handling, and limit data access.
Also, document your compliance with HIPAA, GDPR, or whatever regional rules apply. You don’t want to ship fast and face legal headaches later.
9. Monitor, Improve, and Support
Once live, the job isn’t done. Track how users interact with the system. Look for drop-offs, dead ends, and common failure points.
Use that data to tweak flows or add new ones. Also build a feedback loop. Ask users what worked or what confused them.
Over time, the goal is to reduce support load and increase successful automated outcomes.
Once you've set up the right foundation with clear goals, the right tech stack, clean data, and smooth integration, you're ready to start seeing results. This goes beyond automating tasks. It's about fixing broken workflows, making care more accessible, and scaling without adding overhead.
Types of Conversational AI You Can Use in Healthcare
If you’re building for healthcare, these are the types of conversational AI you’ll come across. Each has its place depending on the kind of problem you’re solving, how flexible the interaction needs to be, and what level of control is required.
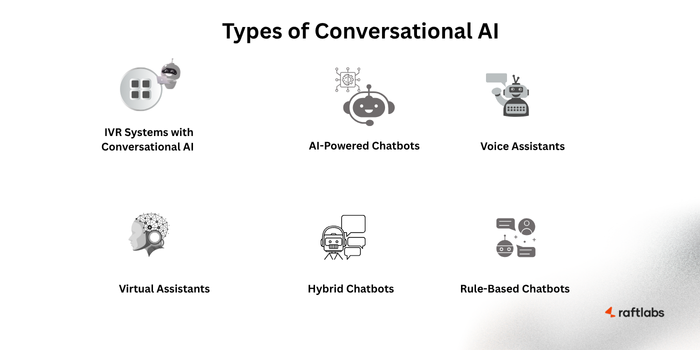
1. Rule-Based Chatbots
These bots work on fixed rules. You define what the user might say, and map responses to each possible input.
They’re easy to set up and reliable for repetitive tasks like appointment confirmations, form filling, or directing users to the right department. But they don’t adapt.
If the user goes off the expected flow or phrases something differently, the bot won’t understand. It will either loop, break, or give a generic fallback message. You can control everything, but it comes at the cost of flexibility.
2. AI-Powered Chatbots
These use NLP and machine learning to understand user intent. They don’t rely on exact matches or predefined paths.
You can feed them examples of how people talk, and they’ll learn patterns over time. These bots are better when the user's inputs are unpredictable.
Things like symptom checkers, onboarding queries, or FAQs with a lot of variety work well here.
They can keep up with real conversations, handle changes in flow, and improve as more users interact with them. But they need more training, good data, and proper testing before going live.
3. Hybrid Chatbots
These combine both rule-based and AI capabilities. You use rules to keep control over critical paths like verifying patient ID, collecting consent, or capturing medical data. Then you let the AI take over for open-ended queries or follow-up questions.
This setup works well in healthcare, where some parts of the flow must be strict and traceable, but others need to feel natural.
Hybrid bots give you the safety of rules and the flexibility of AI in the same workflow. You reduce risks while still giving users a smoother experience.
4. Virtual Assistants
Virtual assistants go beyond simple task execution. They are built to help users over longer sessions and across different topics.
A patient could ask about medication, then follow up with a billing question, and the assistant would still stay in context.
They can handle reminders, care instructions, or guide patients through insurance processes.
They are useful when the goal is to support users across a broader care journey, not just a single task. These assistants usually live inside apps or web platforms and are designed to feel like an ongoing support tool.
5. Voice Assistants
Voice assistants are designed for spoken interaction. Users can speak their request, and the assistant responds out loud. This is helpful for patients who are elderly, visually impaired, or not comfortable typing.
Also useful for doctors or nurses who need hands-free access while working. Voice systems work best when the tasks are quick and the environment allows for clear speech input.
It can be used for appointment management, answering questions, or giving instructions after discharge. It reduces friction and makes digital health tools easier to use for more people.
6. IVR Systems with Conversational AI
Traditional IVRs use menu-based navigation. Users press numbers to select options. When combined with conversational AI, these systems can understand natural speech and guide users through voice commands.
For example, instead of "press 1 for billing," users can say "I want to check my bill." It shortens call times and improves the experience. These setups are useful in call centers handling thousands of routine calls per day.
They take the load off human agents and help patients get answers faster. They are usually deployed in hospitals, diagnostics chains, or insurance hotlines.
Each of these types has a role. Choosing the right one depends on how structured your workflows are, how flexible your user input needs to be, and how much time you have to train and maintain the system.
Challenges of Conversational AI in Healthcare
While conversational AI in healthcare is transforming patient care and operations, implementing it comes with its own set of hurdles. Knowing these challenges upfront helps you design smarter solutions and avoid expensive mistakes later.
1. Data Privacy and HIPAA Compliance
Protecting patient data isn’t optional. Conversational AI systems must meet strict standards like HIPAA and GDPR to ensure sensitive health information stays secure and compliant with regulations.
2. Accuracy and Reliability
AI that gives wrong advice or misses symptoms can harm patients. Babylon Health’s chatbot once made headlines for suggesting a heart attack patient might just have a panic attack. It’s a reminder that robust testing and clinical oversight are critical before deploying in live healthcare environments.
3. Language and Cultural Nuance
Patients come from diverse backgrounds. AI needs to handle different languages, dialects, and cultural sensitivities to deliver care that feels personal and inclusive.
4. Integration with Existing Systems
Healthcare runs on legacy EHRs, billing systems, and CRMs. Seamlessly connecting AI tools to these platforms is often complex but essential for smooth workflows.
5. Patient Trust and Adoption
Many patients are still wary of bots in healthcare. Building trust requires clear communication, easy opt-ins, and the ability to escalate to a human when needed.
6. Regulatory Oversight
Healthcare AI faces strict and evolving rules. Staying ahead of legal and ethical requirements is key to scaling safely and avoiding compliance issues.
7. Digital Literacy Gaps:
Not every patient is tech-savvy. Conversational AI must work across devices and channels to ensure equitable access for all demographics, including elderly and rural populations.
Understanding these challenges early helps founders and product teams design AI that’s not just innovative but also safe, compliant, and patient-centric.
Real-World Examples and Emerging Trends
Real-World Examples
After looking at the challenges, it’s worth seeing how leading healthcare organizations are already putting conversational and voice AI to work.
Northwell Health Chatbot for Care Coordination
Northwell’s conversational Health Chats help patients prepare for procedures like colonoscopies, check in on symptom reporting, and gather social health data. These interactions achieved a 97% patient satisfaction rate and cut follow-up outreach costs by reducing manual calls
Wysa Mental Health Companion
Wysa is an AI-driven conversational agent that provides text-based emotional support, using evidence-based techniques like CBT.
With over 6 million users globally, Wysa demonstrates high engagement and trust, offering real-time mental wellness tools plus safe escalation pathways.
These examples show how the right implementation can solve long-standing problems like improving patient access, easing staff workloads, and delivering measurable impact across healthcare systems.
Emerging Conversational AI Trends In Healthcare
1. Proactive and Predictive AI Engagement
Conversational AI solutions are moving from reactive to proactive, reaching out to patients based on real-time health data, upcoming appointments, or risk modeling.
This shift enables automated appointment reminders, medication refill prompts, and follow-ups without patients having to initiate the interaction.AI can analyze patient data from wearables or EHRs to suggest next steps for care or schedule interventions before a crisis emerges.
2. Personalization and Context Awareness
Systems tailored to individual medical histories, communication preferences, and languages, delivering highly personalized advice and educational content.
AI adapts responses for cultural nuance, tone, and even the preferred channel of communication, improving patient trust and engagement.
3. Multilingual and Multimodal Conversations
Growing emphasis on language diversity, with real-time translation, voice recognition, and region-specific content support expanding equitable healthcare access.
Conversational AI increasingly supports seamless communication across chat, voice, and visual channels, providing consistent healthcare experiences regardless of the medium.
4. Agentic and Autonomous AI Systems
Advanced systems are not just executing single tasks—they’re managing complex workflows, from clinical coding to care coordination and decision support. Autonomous agents can suggest treatments, flag anomalies, and support both patients and clinicians with real-time insights.
Hybrid human-AI teams are evolving, where AI handles repetitive or data-driven tasks, enabling clinicians to dedicate more time to patient interaction.
5. Enhanced Data Integration and Scalability
Conversational AI platforms are now deeply integrated with EHR systems, billing, scheduling, and remote monitoring tools, streamlining both administrative and clinical workflows.
Expanded scalability empowers healthcare organizations to manage a greater volume of patient interactions, crucial for supporting chronic disease management and managing aging populations.
6. Focus on Governance, Privacy, and Regulatory Compliance
With widespread use, there is a growing focus on transparent, explainable AI, along with strict adherence to patient data privacy and local regulatory frameworks.
AI governance is becoming a key differentiator among providers and vendors, ensuring ethical and safe use in patient care.
7. Growth in Patient-Led, Self-Service Healthcare
Empowering patients to manage appointments, access medical records, ask questions, and conduct symptom checks independently, reducing operational bottlenecks and enhancing satisfaction.
These emerging trends reflect how conversational AI has matured from basic automation to a future-ready infrastructure driving efficiency, engagement, and personalized care for both patients and providers in healthcare
Our Case Study: AI-Driven Remote Patient Monitoring for Chronic Care
We helped PDC team enhance their remote patient monitoring (RPM) platform with advanced AI and voice technology to deliver smarter, more accessible care for chronic conditions like hypertension, heart failure, and diabetes.
The solution, built to be HIPAA-compliant and scalable, uses AI to automate data analysis, flag high-risk patients faster, and provide personalized health insights.
To make the platform more patient-friendly, especially for elderly users, we added Voice AI features. Patients can log vitals, receive care instructions, and interact with the system hands-free.
This upgrade positioned PDC as a leader in virtual care, helping providers deliver proactive, real-time support while reducing clinician workload.
Read the full case study to see how we built it.
Wrapping Up
Many healthcare teams rush into conversational AI with generic chatbots that don’t connect to real workflows. Others overcomplicate the tech and lose sight of what patients and staff actually need day to day.
The smarter approach is to focus on one high-value use case first, like automating appointment scheduling, triaging patient queries, or enabling remote monitoring.
Build around real patient behavior and make sure your AI integrates cleanly with EHRs, billing systems, and existing tools.
Teams that get this right are already scaling care, cutting admin load, and creating better experiences for both patients and providers.
If you’re planning to add conversational AI to your healthcare platform, let’s map out the right strategy together.
Frequently Asked Questions
It helps providers scale patient interactions, automate routine tasks like scheduling and triage, and free up staff time, all while improving patient satisfaction and reducing operational costs.
Unlike simple rule-based chatbots, conversational AI is built to handle complex healthcare workflows and patient interactions. Here’s what sets it apart:
Understands natural language and context, not just keywords
Handles multi-step conversations without breaking flow
Connects to EHRs, billing, and scheduling systems for real actions
Learns and improves over time instead of staying static
Yes, if designed correctly. Solutions must comply with HIPAA, GDPR, and use encryption to secure data. Choosing healthcare-focused AI platforms ensures compliance and patient trust.
Modern AI platforms can support regional languages and understand diverse accents, making care more accessible for multilingual and global patient populations.
It typically takes 1 to 2 months to build an MVP with core features like appointment booking or symptom triage. A full-featured product with voice support and backend integrations can take 3 to 4 months to develop and deploy.
Starting small lets you test real workflows, gather user feedback early, and scale with confidence without overbuilding upfront.



